Filler Metal F No
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({
google_ad_client: “ca-pub-7169364926257281”,
enable_page_level_ads: true
});
ASME P Number
The F number grouping of filler metals refers to their similarity on their usability characteristics. The usability determines the ability of a welder to deposit a sound weld metal with a certain filler metal. For Non-impacted test applications only, filler metal classification within an SFA specification, with the same F-number and the same A-number and the same minimum tensile strength and the same. Alloy: UNS: Specifications: AWS/ASME: AMS: Other: HAYNES® 25: R30605-AMS 5796-HAYNES® 82: N06082: SFA / A 5.14 (ERNiCr-3) AMS 5836-HAYNES® 188: R30188-AMS 5801.
To reduce the number of welding and brazing procedure qualifications required base metals have been assigned P-Numbers by the ASME BPVC. Ferrous metals which have specified impact test requirements have been assigned Group Numbers within P-Numbers.

These assignments have been based on comparable base metal characteristics, such as:
- Composition
- Weldability
- Brazeability
- Mechanical Properties
Indiscriminant substitution of materials in a set of P-Numbers or Group Numbers may lead to problems or potentially failures. Engineering assessment is necessary prior to a change in materials.
When a base metal with a UNS number Designation is assigned a P-Number, then a base metal listed in a different ASME material specification with the same UNS number shall be considered that P-Number.
The table below is a guide and is for instructive purposes only. Anyone specifying materials or requirements should refer directly to the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code to specify materials.
| P-Numbers | Base Metal (Typical or Example) |
| 1 | Carbon Manganese Steels (four Group Numbers) |
| 2 | Not Used |
| 3 | Half Molybdenum or half Chromium, half Molybdenum (three Group Numbers) |
| 4 | One and a quarter Chromium, half Molybdenum (two Group Numbers) |
| 5A | Two and a quarter Chromium, one Molybdenum |
| 5B | Five Chromium, half Molybdenum or nine Chromium, one Molybdenum (two Group Numbers) |
| 5C | Chromium, Molybdenum, Vanadium (five Group Numbers) |
| 6 | Martensitic Stainless Steels (Grade 410, 415, 429) (six Group Numbers) |
| 7 | Ferritic Stainless Steels (Grade 409, 430) |
| 8 | Austenitic Stainless Steels · Group 1 – Grades 304, 316, 317, 347 · Group 2 – Grades 309, 310 · Group 3 – High Manganese Grades · Group 4 – High Molybdenum Grades |
| 9A, B, C | Two to four Nickel Steels |
| 10A, B, C, F | Various low alloy steels |
| 10H | Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steel (Grades 31803, 32750) |
| 10I | High Chromium Stainless Steel |
| 10J | High Chromium, Molybdenum Stainless Steel |
| 10K | High Chromium, Molybdenum, Nickel Stainless Steel |
| 11A | Various high strength low alloy steels (six Group Numbers) |
| 11B | Various high strength low alloy steels (ten Group Numbers) |
| 12 to 20 | Not Used |
| 21 | High Aluminum content (1000 and 3000 series) |
| 22 | Aluminum (5000 series – 5052, 5454) |
| 23 | Aluminum (6000 series – 6061, 6063) |
| 24 | Not Used |
| 25 | Aluminum (5000 series – 5083, 5086, 5456) |
| 26 to 30 | Not used |
| 31 | High Copper content |
| 32 | Brass |
| 33 | Copper Silicone |
| 34 | Copper Nickel |
| 35 | Copper Aluminum |
| 36 to 40 | Not Used |
| 41 | High Nickel content |
| 42 | Nickel, Copper – (Monel 500) |
| 43 | Nickel, Chromium, Iron – (Inconel) |
| 44 | Nickel, Molybdenum – (Hastelloy B2, C22, C276, X) |
| 45 | Nickel, Chromium |
| 46 | Nickel, Chromium, Silicone |
| 47 | Nickel, Chromium, Tungsten |
| 47 to 50 | Not Used |
| 51, 52, 53 | Titanium Alloys |
| 61, 62 | Zirconium Alloys |
ASME F Number
The F-number grouping of electrode and welding rod in QW-432 is based essentially on their usability characteristics, which fundamentally determine the ability of welders to make satisfactory welds with a given filler metal. This grouping is made to reduce the number of welding procedure and performance qualifications, where this can logically be done. The grouping does not imply that base metals or filler metals within a group may be indiscriminately substituted for a metal which was used in the qualification test without consideration of the compatibility of the base and filler metal from the standpoint of metallurgical properties, PWHT design and service requirements, and mechanical properties.
| F Number | General Description |
| 1 | Heavy rutile coated iron powder electrodes :- A5.1 : E7024 |
| 2 | Most Rutile consumables such as :- A5.1 : E6013 |
| 3 | Cellulosic electrodes such as :- A5.1 : E6011 |
| 4 | Basic coated electrodes such as : A5.1 : E7016 and E7018 |
| 5 | High alloy austenitic stainless steel and duplex :- A5.4 : E316L-16 |
| 6 | Any steel solid or cored wire (with flux or metal) |
| 2X | Aluminium and its alloys |
| 3X | Copper and its alloys |
| 4X | Nickel alloys |
| 5X | Titanium |
| 6X | Zirconium |
| 7X | Hard Facing Overlay |

Note:- X represents any number 0 to 9
Reference: iiwindia literature and ASME Section IX
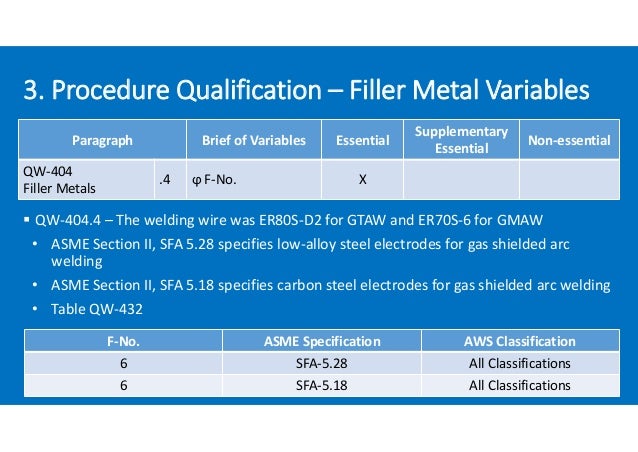
Filler Metal F-no 6
Keep reading, happy welding
Thank you,
Filler Metal F Novak
KP Bhatt
Filler Metal F No
In AWS D1.1 there is NO F-6 listed as an F number in Table 4.13 so it does not apply. Table 4.12 item 2 specifically says 'To an SMAW Electorde with an F-number higher.......) indicating F number is only an consideration for SMAW
ASME handles F Numbers differently and for tyhe most part says the same thing but addresses more Fnumbers.
Regardless, F Number is NOT the only consideration. For any of the variables to work within their range, all other variables must be within the range of qualification. Keep the same F Number but change another variable (Position, Process, Thickness, Backing, Progressions, etc...) In you example below you refer to F6 which is NOT an SMAW F Number but then you refer to 7018. In that case the statement changes the process so another variable is changed.
If you are not intimately familar with 'The codes' I would strongly caution questioning anyone else in a production setting until you become more familar.
As far as D1.1 Clause 4 will address what you need to know regarding variables for performance qualification.
Gerald Austin